October 2020
Mushtaq Ahmed looks at how the cash accounting scheme works
Bridge experience gap between AAT theory and practice
with Future Connect Training at: fctraing.org/aat.php
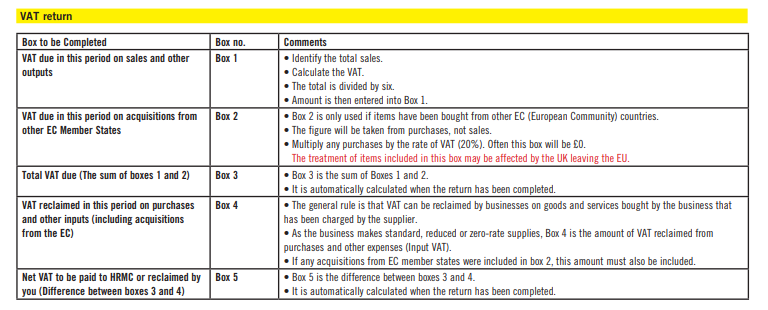
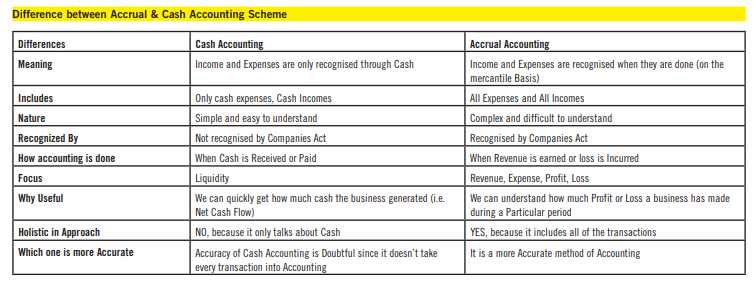
What is Cash Accounting Scheme?
• The Cash Accounting VAT Scheme is a method of reporting VAT on the basis of payments made or received. (Debitoor.com)
• Usually, the amount of VAT you pay HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) is the difference between your sales invoices and purchase invoices.
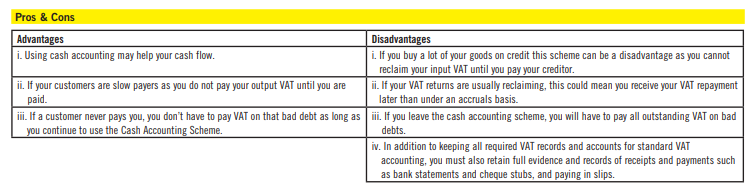
With the Cash Accounting Scheme, you:
i. pay VAT on your sales when your customers pay you
ii. reclaim VAT on your purchases when you have paid your supplier
How to join:
• You must be eligible to join the scheme.
• You join at the beginning of a VAT accounting period.
• You don’t have to tell HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) you use cash accounting (Gov.uk.).
How to leave:
• You can leave the scheme at any time.
• You must leave if you’re no longer eligible to use it, leave at the end of a VAT accounting period.
• You must report and pay HMRC any outstanding VAT (whether your customers have paid you or not).
• You can report and pay the outstanding VAT over 6 months.
• If your VAT taxable turnover exceeded £1.35 million in the last 3 months you must report and pay straight away.
• You must pay immediately if HMRC has written to you to withdraw your use of the scheme.
You are eligible for cash accounting if:
• Your business is registered for VAT.
• Your estimated VAT taxable turnover is £1.35 million or less in the next 12 months.
• You must leave the scheme if your VAT taxable turnover is more than £1.6 million.
You can’t use (exceptions) cash accounting if:
• You use the VAT Flat Rate Scheme – instead, the Flat Rate Scheme has its own cash-based turnover method.
• You’re not up to date with your VAT Returns or payments.
• You’ve committed a VAT offence in the last 12 months, for example VAT evasion.
You can’t use it for the following transactions use standard scheme instead:
• Where the payment terms of a VAT invoice are 6 months or more.
• Where a VAT invoice is raised in advance.
• Buying or selling goods using lease purchase, hire purchase, conditional sale or credit sale.
• Importing goods from within the EU.
• Moving goods outside a customs warehouse.
• Mushtaq Ahmed is the accounts training manager at Future Connect Training